Tuesday 19 July 2011
Friday 8 July 2011
Why does bad software get released?
Why does bad software get released?
Have you ever come across a piece of software that just does not work and wonder, ‘How the heck did this get released?’
Or maybe you have actually worked on a project were you tell the powers to be that the software should not be released, but lo and behold, they go and do it anyway. I had cause to reflect on this question just recently …….. why does bad code get released?
There are of course a myriad of reasons and circumstances that lead to poor code being released, however once cause can be the company culture.
If developers are highly valued, and testers are seen of less value, then it is easy to see why the voice of the tester can go unheard and their view ignored or trodden over.
If testers are no tsufficiently technical or unable to write a coherent and convincing report, their message can get shot down in the general debate, or considered of little value due to the poor presentation.
If the release decision is taken place behind closed doors with no opportunity for the test report to be presented and discussed then the information regarding the true
state of the software might never be made available to those making the decisions.
Of course, there may be a number of reasons why, even though the test report is fully understood, the release is still sanctioned and bad code is released. However these tend to be few and far between
in my experience, the main reason is that the test department of one reason or another is excluded from the process.
Who do I blame? The test department. We need to do more to ensure we are respected, valued and listened to.
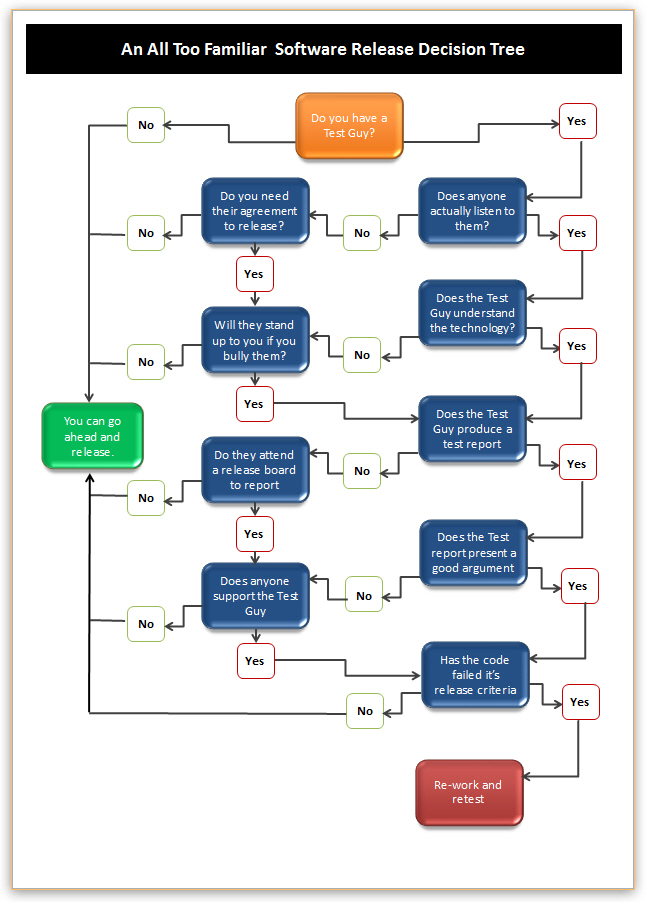
The chart below takes a slightly tongue in cheek look at an all too familiar release decision tree.
Interested article, original posted by: TONY SIMMS - TEST MANAGER
Thursday 21 April 2011
Monday 21 March 2011
Postgresql database configuration for Jmeter GUI mode
Hi everyone, I know some geeks might be searching for the postgresql database configuration for Jmeter GUI mode on Google, like I was looking it before when I started testing the postgresql.
It is very easy! How? Let see.
First download the postgresql driver class for JMeter. There are two driver classes available on postgresql website. JDBC3 Postgresql Driver, Version 9.0-801 this driver class only supports JVM 1.4 version, SSL and the javax.sql package. If you are using 1.6 JVM, like me then go for JDBC4 Postgresql Driver, Version 9.0-801. Once you download the driver class then paste it into “C: / JMeter / lib”.
Now start/open the JMeter, you will see two things (Test Plan and WorkBench). Now right click on the Test Plan --> Add --> Config Element --> JDBC Connection Configuration. JDBC Connection Configuration will be added under Test Plan.
Click on the JDBC Connection Configuration and enter “Postgresql” under variable name field. You will be using this variable in your all database requests. Now enter“10” in Max Number of Connections, “10000” in pool timeout, “60000” in Idle cleanup interval (ms), set Auto Commit to “True”, select “True” for Keep-Alive field, “5000”for Max Connection age (ms), Validation Query “Select1”.
Now under Database Connection Configuration enter following details:
Database URL: jdbc : postgresql : //IPAddress : PortNo/DatabaseName?autoReconnect=true
JDBC Driver class: org.postgresql.Driver
Username: username of database
Password: password of database
Create a Thread Group now by right click on the Test Plan --> Add --> Threads (Users) --> Thread Group. Now under Thread Group add JDBC request by right click on the Thread Group --> Sampler --> JDBC Request. Under JDBC Request enter same Variable Name which we used in the JDBC Connection Configuration “Postgresql”.
Now type your own query or (select * from tablename ; ) and see the result in “View Result Tree”.
Hurray! we have done the configuration for Postgresql in JMeter. Now you can do whatever you want.
EXCEPT DROP :-)
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)